#ThursdayThoughts
As promised, each Thursday, we will now offer you a piece of educational, science, or research related information. The purpose of our #ThursdayThoughts post is to share with you fact-based content that can enlighten and assist you on your fertility journey. Enjoy our post! Helping to Create New Beginnings….
Ovarian Reserve and Fertility
Ovarian reserve refers to both egg quantity and quality. Women are already born with all the eggs they will have in their lifetime. Approximately 1-2 million eggs are present at birth and can be found in each ovary. Over time, the quantity and quality of eggs diminish. At puberty, a woman’s ovaries contain approximately 300,000-500,000 eggs. With each menstrual cycle, the body recruits a group of eggs or follicles, though only one single follicle reaches ovulation in a normal menstrual cycle. The recruited follicles which did not achieve ovulation become atretic (breakdown and are resorbed). Over time, the number of follicles that are recruited each month diminish.
A normal or euploid egg will have 23 chromosomes. When fertilized by sperm, which also has 23 chromosomes, it results in a normal embryo for a total of 46 chromosomes. An abnormal egg may divide inappropriately, resulting in embryos that have a different number of chromosomes. As women age, the number of abnormal eggs also increase. The age of an egg can greatly influence the chances of pregnancy. At age 25, 75% of eggs are chromosomally normal, age 35 about 50% are normal, and by age 40 only 10-15% of eggs are normal. A woman diagnosed with diminished ovarian reserve may have a lower number and quality of eggs expected for her age. In addition to age, endometriosis, pelvic infections, and chemotherapy can affect ovarian reserve. In a study conducted in 2013, Fusi et al. showed that DHEA supplementation can improve ovarian reserve and function. This was mainly demonstrated in a group of women who were poor responders to fertility treatment, and women over the age of forty.
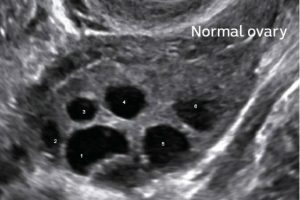
Ovarian reserve testing includes blood tests and a transvaginal ultrasound. Blood tests include hormones such as follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol (E2), and anti-mullerian hormone (AMH). When undergoing fertility treatment, AMH is an important value in predicting ovarian response to treatment. A transvaginal ultrasound provides an antral follicle count which gives us information regarding how many eggs are active in one cycle. Blood tests and an ultrasound are routine components of an initial appointment at the Fertility Institute of Hawaii. For more information regarding diminished ovarian reserve, please visit our website at https://www.ivfcenterhawaii.com/ or call 808-545-2800 to schedule an appointment with one of our physicians.
Francesco M. Fusi, Marina Ferrario, Chiara Bosisio, Mariangela Arnoldi & Laura Zanga (2013) DHEA supplementation positively affects spontaneous pregnancies in women with diminished ovarian function, Gynecological Endocrinology, 29:10, 940-943, DOI: 10.3109/09513590.2013.819087.
Gleicher N, Weghofer A, Barad DH. Defining ovarian reserve to better understand ovarian aging. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011;9:23. Published 2011 Feb 7. doi:10.1186/1477-7827-9-23
La Marca A, Sighinolfi G, Radi D, et al. Anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) as a predictive marker in assisted reproductive technology (ART). Hum Reprod Update. 2010;16(2):113‐130. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmp036